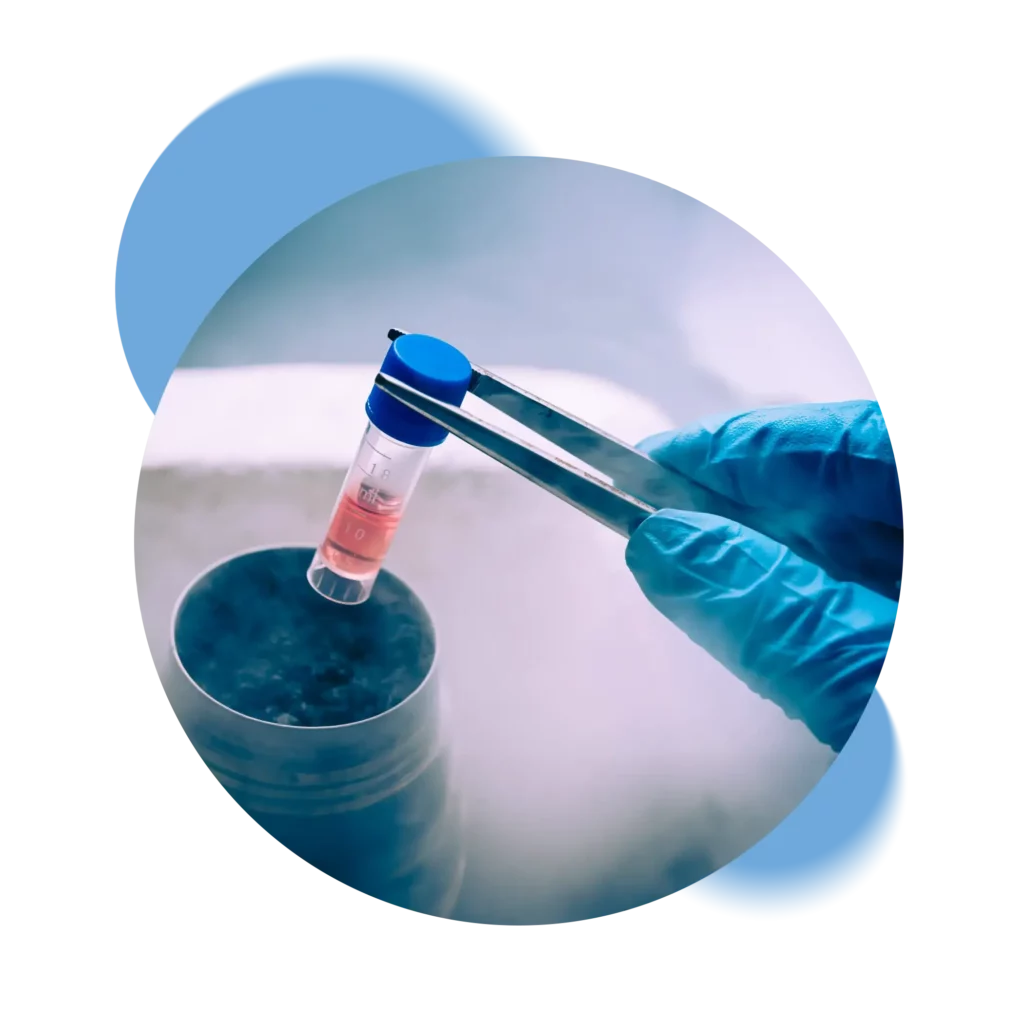
Switzerland’s only private Biobank that processes and stores samples exclusively in its own laboratory without going through intermediaries.
About Us
Swiss Stem Cells Biotech (SSCB), founded in 2005 in Lugano, Switzerland, is the only Swiss private biobank that is FACT-NetCord accredited and GMP certified. Following strict Swiss regulations, SSCB is involved in cryopreservation of stem cells from cord blood, cord tissue and adipose tissue. SSCB is the only Biobank to collaborate in the public-private hybrid banking pilot project.
Through this pilot project, samples processed at SSCB can be listed anonymously in the World Marrow Donor Association (WMDA) global registry and thus made available for worldwide sympathetic use.


Expertise
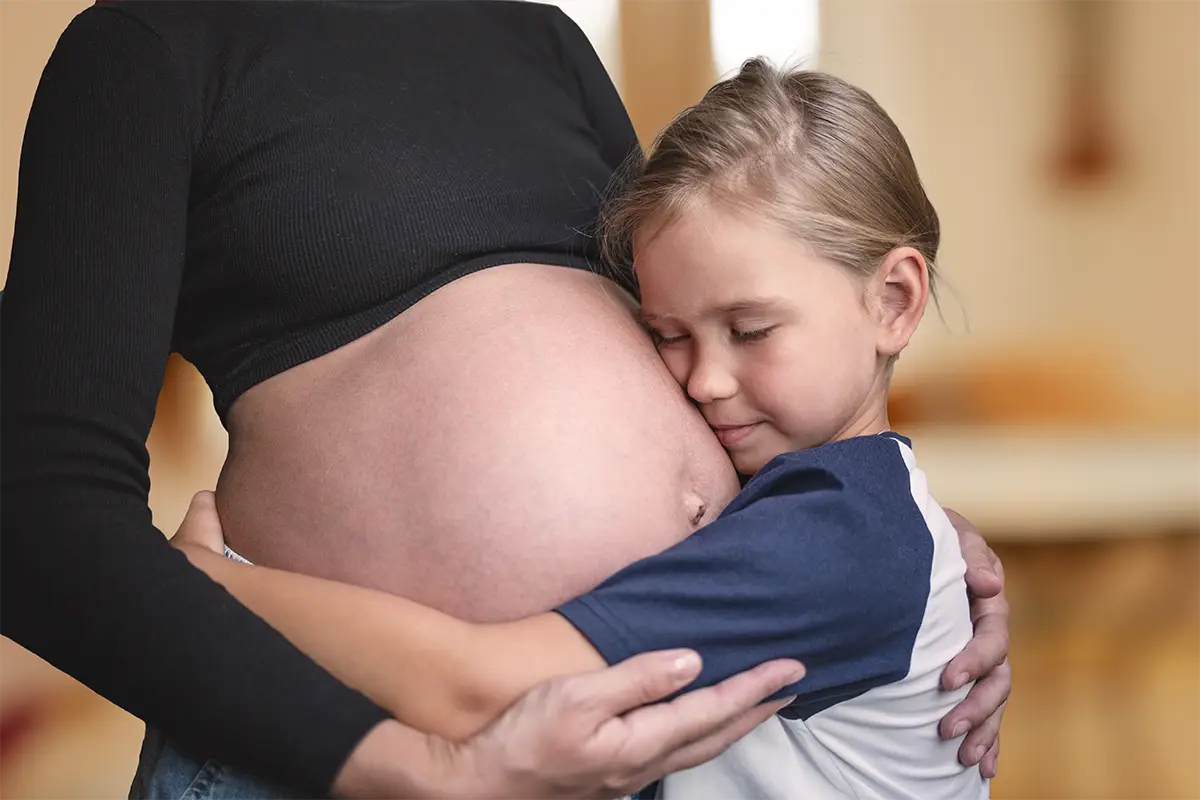
Storing umbilical cord stem cells represents an act of love for your baby. These cells have the ability to differentiate into various cell types, offering an unparalleled opportunity in the field of medicine.
A vital resource for medicine, with applications for established therapies in more than 80 diseases and potential applications in hundreds of clinical trials.
A strategic choice to secure a wide range of future treatments by harnessing the potential of mesenchymal stem cells in different medical fields.
A crucial process for preserving one's genetic code, crucial for future medical applications, personalized research and treatments.
Consultation, development, validation, approval, and production, as well as storage in nitrogen vapor, of products in the field of tissue engineering and advanced biological products (Advanced Therapy Medicinal Products, ATMPs) on behalf of third parties.
Reliability
We ensure complete control of all stages of the cryopreservation process, from kit retrieval, through laboratory processing to storage in our tanks. Each step is certified and recorded so that the status of the samples can always be verified.

The only international certification dedicated exclusively to umbilical cord banking

Thanks to this certification, our products have the same quality level as pharmaceutical products.
By choosing SSCB you will opt for a biobank that is committed to exploring the new frontiers of medicine.
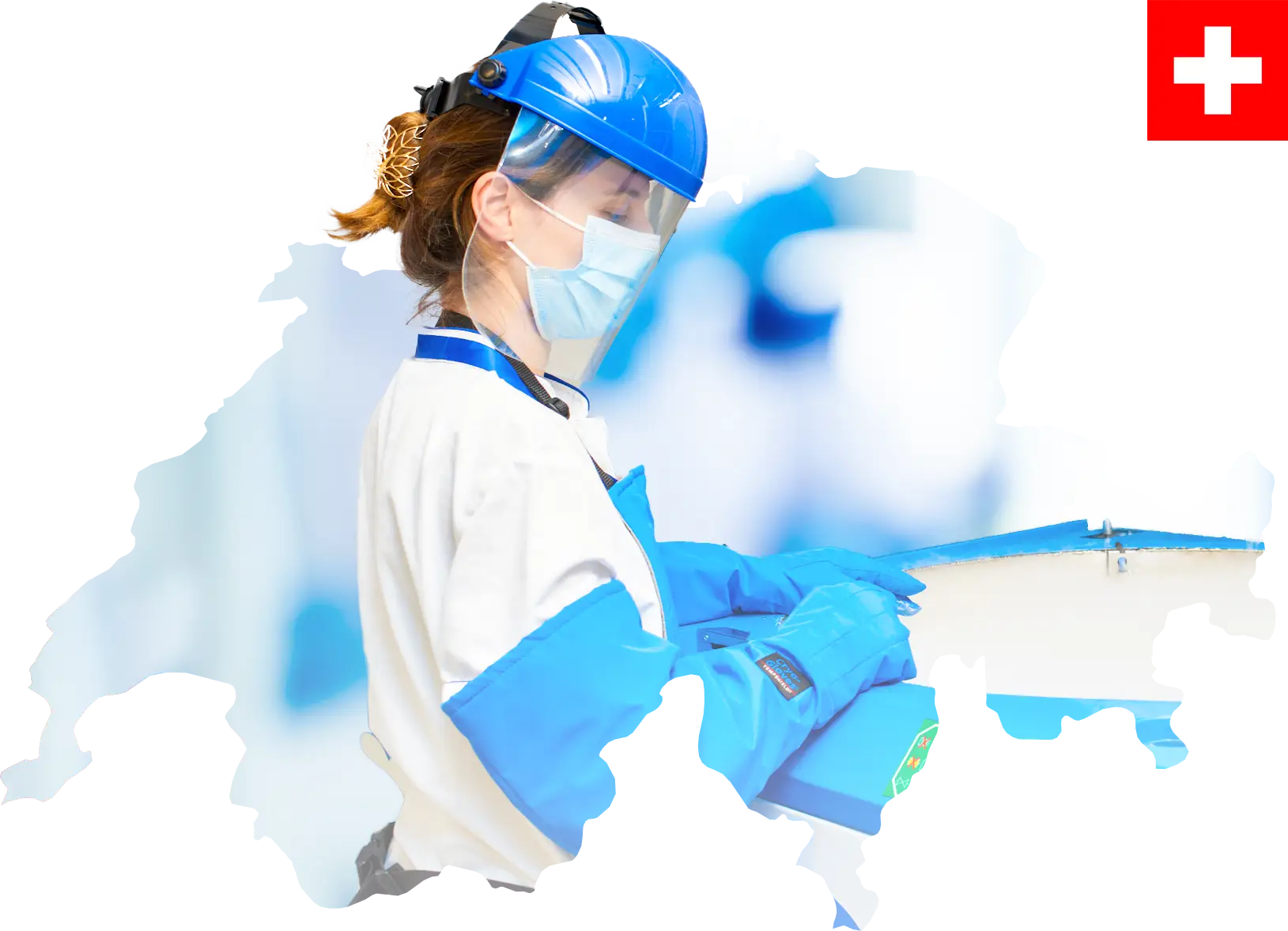
International Presence
Our global network extends across Europe. Each location and partner reflects our commitment to excellence, working closely together to deliver high-quality, safe services and solutions.

Certified Swiss Biotech company a leader in stem cell preservation.
